

9 This occurs when local anesthetic is introduced systemically instead of locally. IVFE can be used in the treatment of local anesthetic systemic toxicity (LAST). 4, 5 Caution must be used when administering fat emulsion to neonates because of low rates of clearance and the potential for intravascular accumulation in lungs. The initial dose is usually 1 to 2 g/kg/d and is increased by one-half to 1 g/kg/d to a maximum of 3 g/kg/d.
6 Additionally, the use of IVFE provides a dense calorie source to help decrease the volume of PN required.įat emulsion can also be used for pediatric and neonatal patients. 6 To improve tolerability, doses usually are limited to 1 to 1.5 g/kg/d on day 1 of therapy for adult patients.

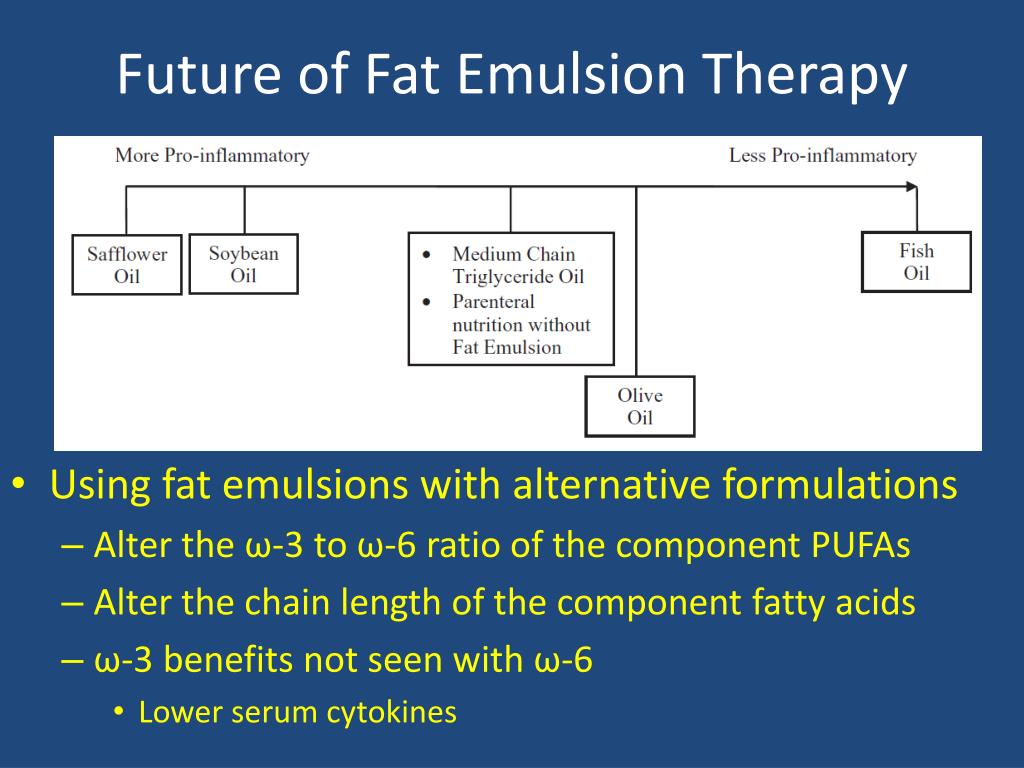
Fat usually makes up about 20% to 30% of nonprotein calories with a maximum of 60% of total calories, or 2.5 g/kg/d. It also can be combined with the amino acids and dextrose in what is called 3-in-1, or total nutrient admixture. 3 For PN, it can be administered separately from the dextrose and amino acid solution (2 in 1). IVFE can be used for several reasons, including the primary use in PN for adults, children, and neonates, as well as for treatment of local anesthetic toxicity and drug overdoses, in which it acts as an antidote. 3 As of August 2015, however, this product had not yet become available on the market in the United States. 6 The product would provide a more favorable lipid profile than those currently available on the market. 2 In 2013, the US Food and Drug Administration approved a new product, a mixture of soybean and olive oil called lipid injectable emulsion (Clinolipid Baxter, Deerfield, IL). 2, 3 About 50% of the emulsion is made up of omega-6 fatty acids, as well as 25% omega-3 and 25% omega-9 fatty acids. 4, 5 The soybean oil in these products provides a mixture of omega-6, omega-3, and omega-9 fatty acids. Braun Bethlehem, PA), which are currently available in the United States. They include IVFE Intralipid (Baxter Deerfield, IL), IVFE Liposyn III (Hospira Lake Forest, IL), and IVFE Nutrilipid (B. Since that time, additional products derived from soybean oil have come on the market. 4, 5 So it provided some, but not all, of the essential fatty acids needed for patients dependent on PN to prevent fatty acid deficiency. 3 It consisted of 77% omega-6 fatty acids 2, 3 but lacked ALA, which is an essential fatty acid. The first product available in the United States was released in 1961 and was made from safflower oil. 1 Vitamin E is also added to help reduce the oxidative stress of the emulsion components, as well as the oxidative stress on patients. In addition, alpha linolenic acid (ALA), which is used as a stabilizing agent for the emulsion, makes up a small percentage of the emulsion. The emulsion is a mixture of 3 fatty acids: omega-6, -3, and -9. Once the emulsion was developed, it was heralded as a breakthrough for patients who required long-term PN and who previously were limited to dextrose and amino acids for sources of their calories. 2 Patients' conditions could be complicated by excessive dextrose intake, which can cause hyperglycemia increased carbon dioxide production hepatic steatosis and phagocyte destruction. The deficiencies can present as cholestasis, steatosis, alopecia, dermatitis, and thrombocytopenia.
1, 2 Before the development of IVFE, patients would develop essential fatty acid deficiencies. Intravenous fat emulsion (IVFE) is a mixture of long-chain fatty acids originally formulated to provide essential fatty acids for patients on parenteral nutrition (PN) and a dense source of calories to help reduce the volume required for PN.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
